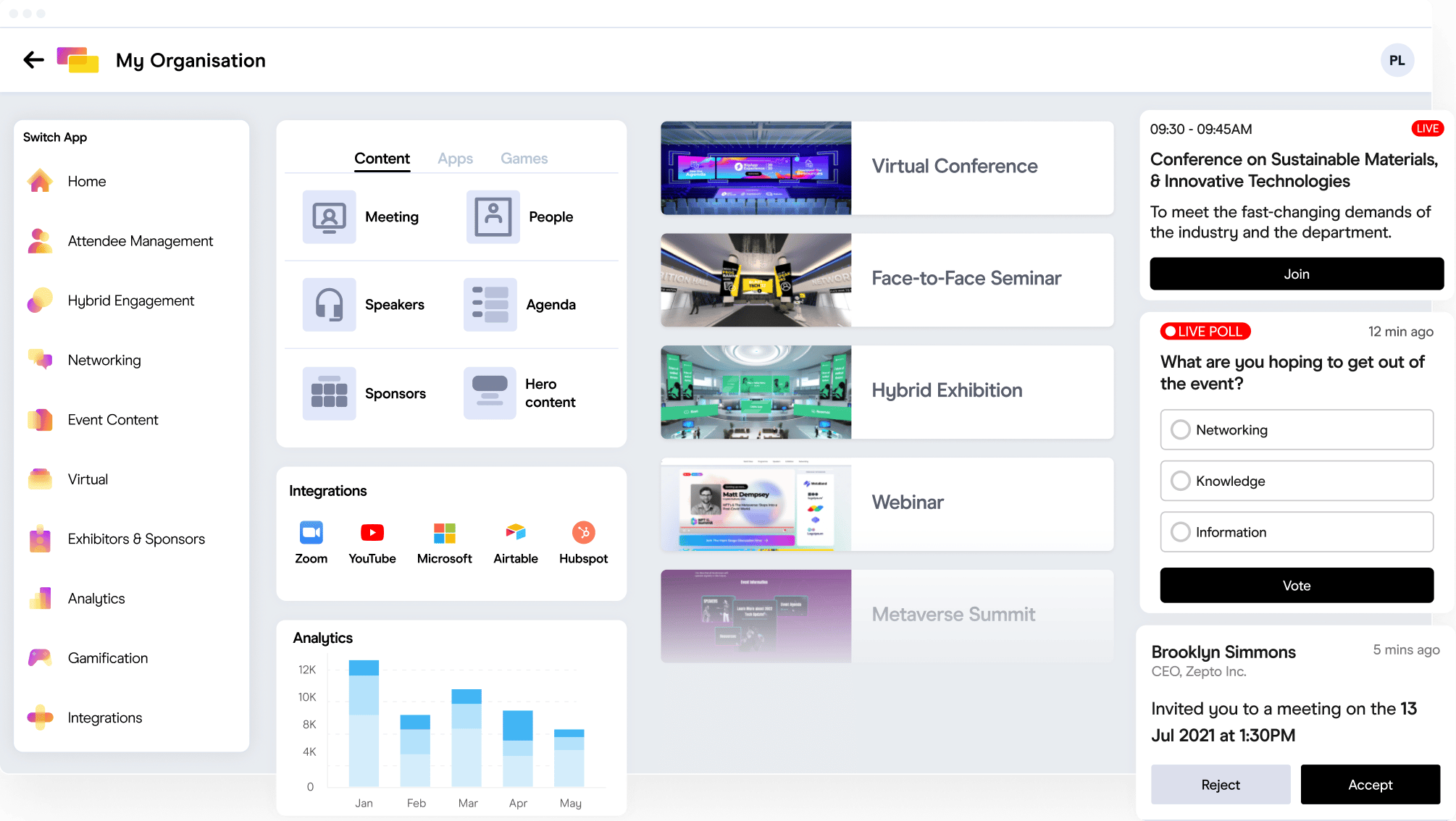
As Artificial Intelligence (AI) becomes increasingly integral to event management, it brings along a complex web of ethical and privacy concerns. The integration of AI in event management, from personalized attendee experiences to data-driven decision making, offers unparalleled efficiency and innovation. However, this advancement also raises significant questions about privacy, data security, and ethical use.
In this blog, we delve into the ethical and privacy challenges posed by AI in event management, exploring how industry professionals can navigate this evolving landscape while upholding the highest standards of responsibility and trust.

Understanding AI in Event Management
AI in event management is reshaping the landscape of event management with its diverse applications:
- Personalized Attendee Experiences: AI’s ability to analyze complex attendee data transforms into highly personalized event experiences. This includes customizing event itineraries, providing targeted content, and even suggesting networking opportunities tailored to individual preferences.
- Data-Driven Event Planning: AI’s role in event planning extends to analyzing large sets of attendee data, offering valuable insights into preferences and behaviors. This data drives strategic decision-making, enabling organizers to tailor events more effectively to their audience.
- Automated Customer Service: Utilizing AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants, event organizers can offer 24/7 customer service. These tools handle a wide range of inquiries, from basic event information to specific attendee requests, providing timely and efficient responses.
- Enhanced Security Measures: In the realm of security, AI is employed for facial recognition for entry management and monitoring crowd dynamics. These applications not only bolster event security but also streamline entry processes, enhancing attendee convenience.
- Efficient Operational Management: AI streamlines various operational aspects of event management. From automating the registration process to optimizing venue logistics and scheduling, AI ensures that events run smoothly and efficiently.
- Marketing and Engagement Analytics: AI tools provide deep insights into marketing effectiveness and attendee engagement. By analyzing engagement patterns, AI helps in refining marketing strategies and enhancing the overall attendee experience.
- Networking and Matchmaking: AI’s sophisticated algorithms can effectively match attendees for networking purposes, based on their professional interests and backgrounds, fostering more meaningful connections at events.

Privacy Concerns with AI
The deployment of AI in event management brings to the forefront a range of privacy concerns:
- Data Collection and Consent: The effectiveness of AI depends on the collection of detailed attendee data. This raises critical questions about informed consent – how attendees are made aware of what data is being collected, the purpose of this collection, and the duration for which their data will be kept.
- Data Storage and Security: Protecting the vast amounts of data collected by AI systems is paramount. Ensuring advanced encryption methods, regular security audits, and adherence to best practices in data security are essential to safeguard against breaches and unauthorized access.
- Data Usage and Sharing: Clarifying how attendee data is utilized is vital. It’s important to establish boundaries regarding data sharing, particularly with third parties, and to ensure that such sharing is compliant with privacy laws and regulations.
- Surveillance and Tracking: The use of AI for surveillance and tracking at events, while beneficial for security and personalization, can encroach on personal privacy. Strict policies and transparency are required to balance the benefits with privacy rights.
- Retention and Deletion of Data: Managing the lifecycle of the data collected is a key privacy issue. Clear policies on data retention and timely deletion of data post-event are necessary to protect attendee privacy.
- Cross-Border Data Transfer: For international events, the transfer of data across borders introduces complexities due to varying data protection laws in different countries. Ensuring compliance with these diverse regulations is crucial.
- Anonymization of Data: Anonymizing data used for analytics is a significant step in safeguarding privacy. It involves stripping away personally identifiable information to prevent the tracing back of data to individual attendees.

Ethical Implications of AI Usage
The incorporation of AI in event management not only enhances capabilities but also brings forth a spectrum of ethical considerations:
- Potential for Bias in AI Algorithms: The risk of AI algorithms inheriting biases from their training data is a significant ethical concern. These biases could lead to discriminatory practices or unequal treatment of certain groups of attendees, raising questions about fairness and equity in AI-driven systems.
- Impact of AI Decisions on Attendees and Stakeholders: AI’s influence extends to various stakeholders, including attendees, sponsors, and organizers. Decisions made by AI, such as personalized content curation or attendee segmentation, can have a substantial effect on their event experience and satisfaction.
- Transparency of AI Systems: The complexity of AI systems often leads to a ‘black box’ scenario, where the decision-making process is opaque. Ensuring transparency in how these systems work and make decisions is crucial to build trust and accountability.
- Consent and Choice in AI Interactions: Respecting attendee autonomy through consent and choice in their interaction with AI-driven services is a key ethical practice. This involves clear options for opting in or out of AI-driven experiences and respecting privacy preferences.
- Accountability for AI Decisions: Establishing accountability for the outcomes of AI decisions is vital. This includes having protocols in place to address any negative impacts or disputes arising from AI’s role in event management.
- Ensuring Dignity and Respect: AI should be leveraged in a manner that upholds the dignity and respect of all attendees. This includes avoiding invasive surveillance methods or the use of AI in ways that might cause discomfort or unease.
- Long-Term Societal Impact: Considering the long-term societal implications of AI in events, such as how it shapes privacy norms and public expectations, is essential for responsible AI usage.
Regulatory Landscape for AI and Privacy
The legal landscape surrounding the use of AI in event management is intricate and multi-faceted:
- Global Data Protection Regulations: Various global regulations, like the GDPR in Europe, impose strict rules on data processing and privacy. These regulations require explicit consent for data collection, limit data usage, and mandate secure data handling practices.
- Compliance with Local Laws: Compliance becomes more complex as event technologies cross borders. Each region or country may have unique privacy laws, requiring AI systems to be adaptable and compliant with these diverse legal requirements.
- Industry-Specific Regulations: Different industries may face unique regulatory demands concerning AI and privacy. For example, healthcare events might need to comply with additional privacy laws like HIPAA in the United States.
- Updates and Changes in Laws: The legal framework for AI and privacy is in a state of flux, with new laws and amendments frequently introduced. Staying abreast of these changes is crucial to ensure ongoing compliance.
- Standardization of AI Ethics and Privacy: There is a growing movement towards the standardization of AI ethics and privacy regulations on a global scale. Such standardization will significantly impact the application of AI in international events.
- Legal Implications of Non-Compliance: Failure to comply with these regulations can lead to severe penalties, including hefty fines, legal action, and damage to the organization’s reputation.
- Role of Legal Teams in AI Implementation: In navigating this complex legal landscape, the role of in-house or external legal teams becomes essential. They are responsible for ensuring that AI implementations in event management adhere to all applicable laws and regulations.
Best Practices for Ethical AI Use
To ensure the ethical use of AI in event management, it’s essential to adopt comprehensive best practices:
- Transparent AI Policies: Develop and communicate clear policies regarding AI use, detailing how algorithms function, data is processed, and decisions are made. This transparency is crucial for building trust among stakeholders.
- Informed Consent: Emphasize obtaining explicit and informed consent from attendees for data collection and use. This involves clearly explaining the purpose of data collection and how it will enhance their event experience.
- Bias Mitigation Strategies: Implement robust strategies to identify and mitigate potential biases in AI algorithms. This includes using diverse data sets for training and regularly reviewing AI decisions for fairness and impartiality.
- Regular Audits for Compliance: Conducting regular audits ensures that AI applications remain compliant with ethical standards and privacy laws. These audits can help identify and rectify potential issues in early stages.
- Privacy by Design Approach: Adopt a privacy by design approach, incorporating privacy considerations into every stage of AI system development. This proactive stance helps in safeguarding attendee data throughout the lifecycle of the event.
- Ethical Training for AI Teams: Provide comprehensive training for teams working with AI in event management, focusing on ethical considerations, privacy concerns, and responsible AI use. This training should include updates on legal and regulatory changes.
- Stakeholder Engagement: Engage actively with stakeholders, including attendees, clients, and partners, to understand and address their concerns about AI use. This engagement is vital for ensuring that AI solutions are aligned with the needs and expectations of all parties involved.
Balancing Innovation with Privacy
Striking the right balance between embracing AI innovations in event management and maintaining attendee privacy is a nuanced process:
- Developing Ethical AI Frameworks: Creating comprehensive ethical frameworks for AI in event management is vital. These frameworks should not only comply with legal standards but also uphold moral and ethical values, guiding how AI is developed and used.
- Incorporating Privacy into AI Design: Integrating privacy considerations into the design and development of AI systems is critical. This approach ensures that privacy protection is not an afterthought but a foundational aspect of AI in events.
- Regular Privacy Impact Assessments: Conducting thorough privacy impact assessments on a regular basis helps in identifying potential privacy risks associated with AI applications. These assessments guide the modification and improvement of AI systems to better protect attendee data.
- Clear Communication with Attendees: Maintaining transparent communication with attendees about privacy practices is essential. This includes explaining how data is collected, used, and protected, and providing clear options for attendees to control their personal data.
- Collaboration with Privacy Experts: Partnering with privacy experts and legal advisors ensures that AI implementations in event management are in line with current privacy laws and best practices, helping to navigate the complex landscape of data protection.
- Technological Safeguards: Implementing advanced technological safeguards, such as encryption and secure data storage, is crucial in protecting attendee data from breaches and unauthorized access.
- Continuous Monitoring and Adaptation: Keeping pace with the evolving nature of privacy challenges requires continuous monitoring of AI systems and adapting to new threats and vulnerabilities as they emerge.

The Role of Event Professionals
The responsibility of event professionals in the ethical and privacy aspects of AI is multifaceted and critical:
- Staying Educated on AI and Privacy: Event professionals must engage in ongoing education about AI advancements and privacy regulations. This involves attending relevant workshops, webinars, and courses to stay abreast of the latest developments.
- Implementing Ethical AI Practices: It’s crucial for event professionals to champion and enforce ethical AI practices. This means ensuring that AI applications are designed and used in ways that respect attendee privacy and adhere to ethical standards.
- Collaborating with Technologists and Legal Experts: Building strong collaborations with AI technologists and legal experts is key. This partnership is essential for understanding the complexities of AI technology and navigating the associated legal landscape.
- Proactive Risk Management: Event professionals should proactively identify and manage potential risks associated with AI. This involves conducting regular risk assessments and developing strategies to mitigate any identified risks.
- Ensuring Transparency and Accountability: Maintaining transparency about how AI is used and ensuring accountability in the event of any issues is vital. This includes clearly communicating with attendees about AI-driven processes and being prepared to address any concerns or incidents.
- Advocating for Attendee Rights: Advocacy for the rights of attendees in the context of AI is a crucial role. Event professionals should ensure that attendee data is not only used responsibly but also that their rights to privacy and data security are upheld.
- Adapting to Changing Regulations: The regulatory environment for AI and privacy is constantly evolving. Event professionals need to be adaptable and responsive to these changes to ensure ongoing compliance.
Conclusion
As we delve into the future of event management, the ethical and privacy concerns surrounding AI present both challenges and opportunities. It’s crucial for event professionals to navigate these issues thoughtfully, balancing the innovative potential of AI with the imperative of safeguarding attendee privacy. Platforms like Gevme are actively integrating AI into their event solutions while also prioritizing these ethical considerations. As the event industry continues to evolve with AI, the commitment to ethics and privacy will not only foster trust but also drive sustainable innovation. Embracing this dual focus is the key to unlocking the full potential of AI in event management.